Going by the LIFO method, Ted needs to go by his most recent inventory costs first and work backwards from there. Assuming Ted kept his sales prices the same (which he did, in order to stay competitive), this means there was less profit for Ted’s https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/ Televisions by the end of the year. These fluctuating costs must be taken into account regardless of which method a business uses. To calculate COGS (Cost of Goods Sold) using the LIFO method, determine the cost of your most recent inventory.
The staff of the Joint Committee on Taxation believes that these reforms, which would be implemented gradually over four years, would increase revenues amounting to a total of $102 billion between 2017 and 2026. However, as is the case in many nations around the globe, the general tendency of the economy is inflationary. This is why the usage of LIFO delivers minimal benefits, and its drawbacks outweigh its positive aspects, given the current state of the economy. Indeed, each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, and how a particular method is judged is contingent upon the present facts and circumstances. This month, Kroger said that it had a LIFO charge of $93 million during the quarter that ended on May 21, compared to a LIFO charge of $37 million during the same period in the prior year. When considering LIFO for your accounting, here is more information on the pros, downsides, and restrictions you must consider.
- LIFO accounting assumes you sell or use your most recent inventory first.
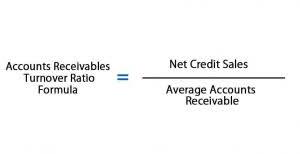
- Brad would now like to run a report for his partners that shows the cost of goods sold.
- Despite this, a corporation is not required to go through the LIFO process flow to apply the approach to assess the value of its inventory.
- Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
- Although the oldest inventory may not always be the first sold, the FIFO method is not actually linked to the tracking of physical inventory, just inventory totals.
- Had the corporation used FIFO, it would have removed $40 from inventory and matched it with the selling price of $60.
The final approach we will investigate is known as the average cost technique, which involves calculating a single cost estimate for all of the inventory. This method of inventory computation is helpful for companies selling a significant quantity of items comparable to one another, such as phone cases. During inflation, LIFO accounting often lowers net income because costs of inventory tend to increase when your raw materials cost more. The Canada Revenue Agency and International Financial Reporting Standards don’t allow the use of LIFO for inventory valuation in terms of financial reporting or tax purposes.
What Does It Mean to Use the LIFO Method?
Depending on the unit cost and timing of inventory transactions, the LIFO method can generate a number of tax benefits due to profitability impacts on the income statement. FIFO has advantages and disadvantages compared to other inventory methods. FIFO often results in higher net income and higher inventory balances on the balance sheet. However, this results in higher tax liabilities and potentially higher future write-offs if that inventory becomes obsolete. In general, for companies trying to better match their sales with the actual movement of product, FIFO might be a better way to depict the movement of inventory.
- However, the company already had 1,000 units of older inventory that was purchased at $8 each for an $8,000 valuation.
- However, please note that if prices are decreasing, the opposite scenarios outlined above play out.
- This would result in a P&L for the current year of $3.00 – the difference between the cumulative LIFO benefits of this and the previous year.
- In addition, supporters contend that a company’s tax bill when it operates under FIFO is unjust (as a result of inflation).
- If you purchased one item at the cost of $5 per unit and another at the cost of $21, you would have an average unit cost of $13, which does not correspond well with either of the prices.
So under FIFO, the cost of goods sold (COGS) for the first sales is $10. That $2 difference would significantly impact the company’s financial statements and tax filing. Choosing FIFO https://bookkeeping-reviews.com/ would have the impact of making its profit appear larger for investors. Conversely, choosing LIFO would have the impact of making its profit appear smaller to the tax authorities.
During times of inflation, LIFO might result in lower tax bills.
However, according to Mr. Berg, Amerco has no plans to change its accounting method despite the higher inflation rates. According to what he said, “our strategy has been to minimize the amount of taxes that we pay” to achieve maximum cash flow. Even though businesses in a wide variety of sectors employ LIFO, the oil industry, in particular, has been criticized for being the one to profit financially from increases in oil prices. When prices fall, the inventory value that businesses deduct as an expense initially drops, which implies that the tax benefits may become less favorable.
Why Should I Use LIFO?
The BLS categories reflect a domestic rate of inflation and do not include offshore manufacturing or overseas purchases. The BLS indexes generally display a higher rate of inflation and, thus, a greater benefit from LIFO. This would result in a P&L for the current year of $3.00 – the difference between the cumulative LIFO benefits of this and the previous year.
But you can still use LIFO accounting to benefit your business for your internal records. LIFO improves income matching statements when you analyze your current expenses. Selling more recent widgets in your inventory matches better with the expenses you incur to buy or produce them. The LIFO method helps you to align your income versus costs during a more recent reporting period versus one from six months ago when you bought the older widgets.
LIFO and FIFO: Financial Reporting
A LIFO liquidation is when a company sells the most recently acquired inventory first. It occurs when a company that uses the last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventory costing method liquidates its older LIFO inventory. A LIFO liquidation occurs when current sales exceed purchases, resulting in the liquidation of any inventory not sold in a previous https://quick-bookkeeping.net/ period. The average cost method takes the weighted average of all units available for sale during the accounting period and then uses that average cost to determine the value of COGS and ending inventory. In our bakery example, the average cost for inventory would be $1.125 per unit, calculated as [(200 x $1) + (200 x $1.25)]/400.
Therefore, the old inventory costs remain on the balance sheet while the newest inventory costs are expensed first. A more realistic cost flow assumption is incorporated into the first in, first out (FIFO) method. This approach assumes that the oldest inventory items are used first, so that only the newest inventory items remain in stock. Another option is the weighted average method, which calculates the average cost for all items currently in stock. Businesses that sell products that rise in price every year benefit from using LIFO.
Below are the Ending Inventory Valuations:
In periods of substantial inflation, those against LIFO argue that it skews the figures used on the balance sheet to represent inventories. They further point out that LIFO provides its users with an unfair tax benefit because it can potentially reduce a company’s net income and, as a result, the company’s taxes. If Company X had just one of these products in the start-of-year and end-of-year inventory, LIFO would yield a tax benefit of $2.00 which represents the difference in the FIFO value ($12) and LIFO value ($10). By using LIFO, Company X increased its Cost-of-Goods-Sold (COGS) by $2 . Simply put – valuing the product in the year-end inventory at LIFO offers an advantage when compared to the FIFO value.
If the company made a sale of 50 units of calculators, under the LIFO method, the most recent calculator costs would be matched with the revenue generated from the sale. It would provide excellent matching of revenue and cost of goods sold on the income statement. For example, consider a company with a beginning inventory of 100 calculators at a unit cost of $5. The company purchases another 100 units of calculators at a higher unit cost of $10 due to the scarcity of materials used to manufacture the calculators. By its very nature, the “First-In, First-Out” method is easier to understand and implement.